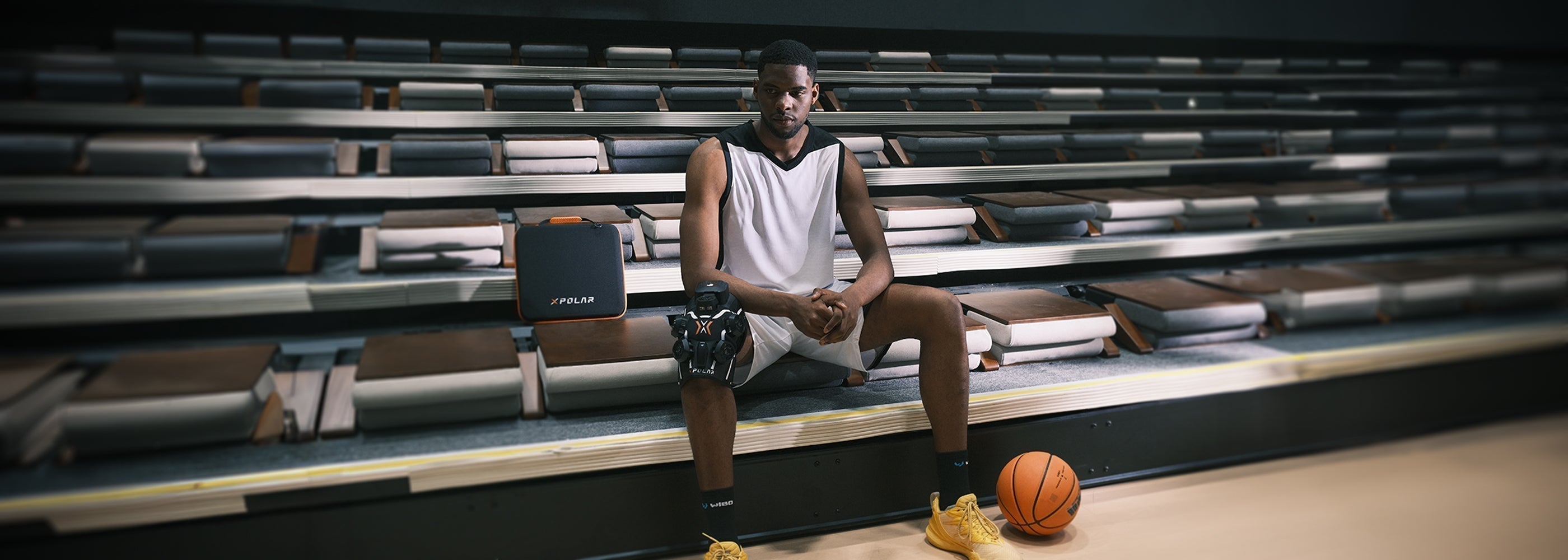
Compression + Cold Therapy Accelerates Recovery After Knee Replacement — New Clinical Evidence
Compressive cryotherapy leads to faster and more significant improvements in knee mobility, pain reduction, and functional performance compared with standard cryotherapy during the first 21 days af...

Tissue physiology and the response to heat
The most important physiological parameter influencing tissue response to heat is blood flow. At mild hyperthermia temperatures blood perfusion increases in many tumours and this effect is heating ...
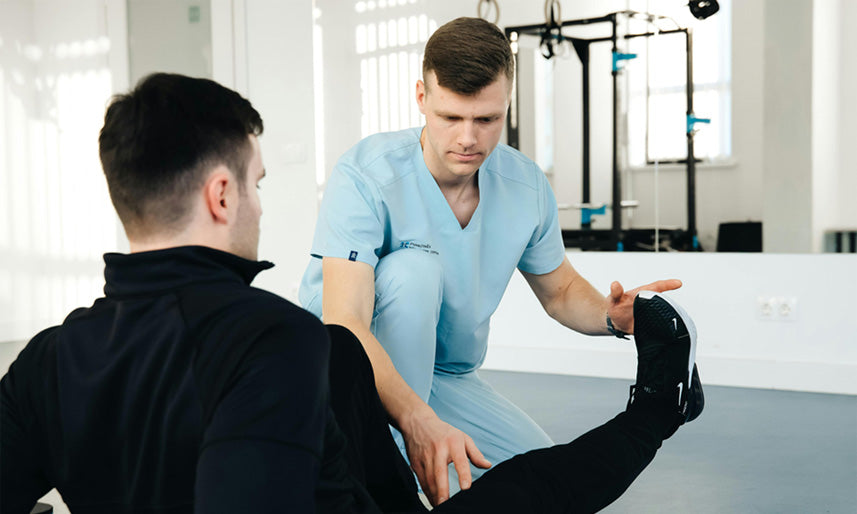

Cold Therapy in Post-Operative Care: Enhancing Healing After Knee Surgery
Cold Therapy for Total Knee Replacement (TKR) Surgery Recovery Cold therapy, also known as cryotherapy, is a highly effective method for managing pain and swelling after total knee replacement (TK...
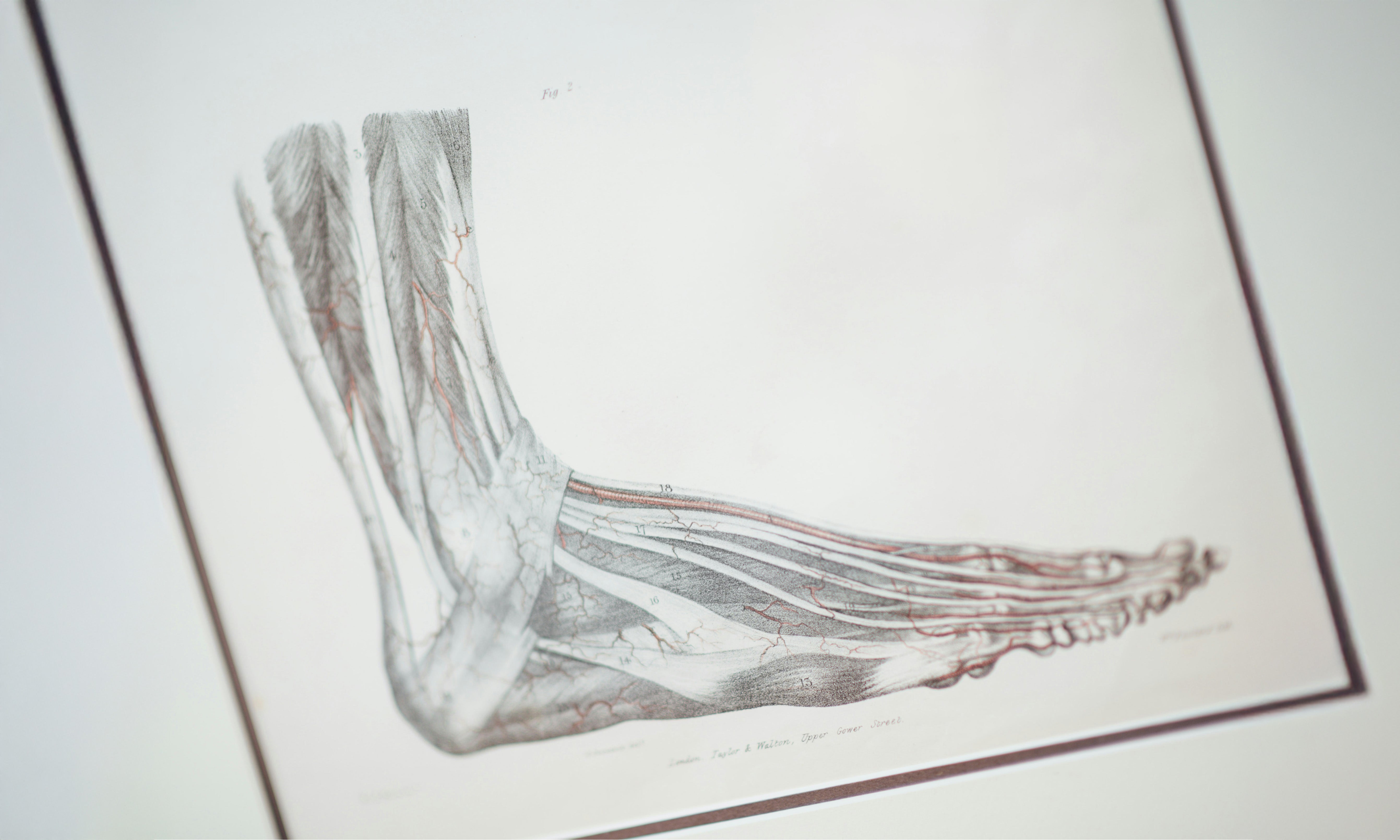
Effect of different thermal stimuli on improving microcirculation in the contralateral foot
Background The lower extremities of the body often suffer from impaired microcirculation, particularly in the elderly or people with underlying conditions such as diabetes. Especially for people su...

How Heat, Cold, and Contrast Therapy Benefit Your Body
Introduction Heat, cold, and contrast therapy have been used for centuries to treat various ailments, from pain relief to reducing swelling. These therapies originated in ancient Greek and Egy...
Introduction This review was conducted at the request of the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) to evaluate the use of pneumatic compression devices in the home environment for treat...








